nengolib.networks.LinearNetwork¶
-
class
nengolib.networks.LinearNetwork(sys, n_neurons_per_ensemble, synapse, dt, radii=1.0, input_synapse=None, output_synapse=None, realizer=Hankel(), solver=Default, label=None, seed=None, add_to_container=None, **ens_kwargs)[source]¶ Network implementing a linear time-invariant (LTI) system.
This network implements the following linear state-space model:
\[\begin{split}\dot{{\bf x}}(t) &= A{\bf x}(t) + B{\bf u}(t) \\ {\bf y}(t) &= C{\bf x}(t) + D{\bf u}(t)\end{split}\]This works by first realizing a state-space representation from the given
sysandrealizer, and then usingss2sim()to apply a generalization of Principle 3 from the Neural Engineering Framework (NEF) to map the system onto the givensynapse. This yields amappedsystem whose state-space matrices give the transformation matrices for the resulting Nengo network.Parameters: - sys :
linear_system_like Linear system representation.
- n_neurons_per_ensemble :
integer Number of neurons to use per ensemble (i.e., per dimension).
- synapse :
nengo.synapses.Synapse Recurrent synapse used to implement the dynamics, passed to
ss2sim().- dt :
floatorNone Simulation time-step (in seconds), passed to
ss2sim(). IfNone, then this uses the continuous form of Principle 3 (i.e., assuming a continuous-time synapse with negligible time-step). If provided, thensyswill be discretized and the discrete form of Principle 3 will be applied. This should always be given for digital simulations.- radii :
floatorarray_like, optional Radius of each dimension of the realized state-space. If a single
float, then it will be applied to each dimension. Ifarray_like, then its length must matchsize_state. Defaults to1.- input_synapse :
nengo.synapses.Synapse, optional Input synapse connecting from
inputnode. Defaults toNoneto discourage double filtering, but should typically match thesynapseparameter.- output_synapse :
nengo.synapses.Synapse, optional Output synapse connecting to
outputnode. Defaults toNone.- realizer :
AbstractRealizer, optional Method of obtaining a state-space realization of
sys. Defaults toHankel.- solver :
nengo.solvers.Solver, optional Solver used to decode the state. Defaults to
nengo.solvers.LstsqL2(withreg=.1).- label : str, optional (Default: None)
Name of the network.
- seed : int, optional (Default: None)
Random number seed that will be fed to the random number generator. Setting the seed makes the network’s build process deterministic.
- add_to_container : bool, optional (Default: None)
Determines if this network will be added to the current container. If None, this network will be added to the network at the top of the
Network.contextstack unless the stack is empty.- **ens_kwargs :
dictionary, optional Additional keyword arguments are passed to the
nengo.networks.EnsembleArraythat represents thestate.
See also
Notes
By linearity, the
input_synapseand theoutput_synapseare interchangeable with one another. However, this will modify the state-space (according to these same filters) which may impact the quality of representation.Examples
>>> from nengolib.networks import LinearNetwork >>> from nengolib.synapses import Bandpass
Implementing a 5 Hz
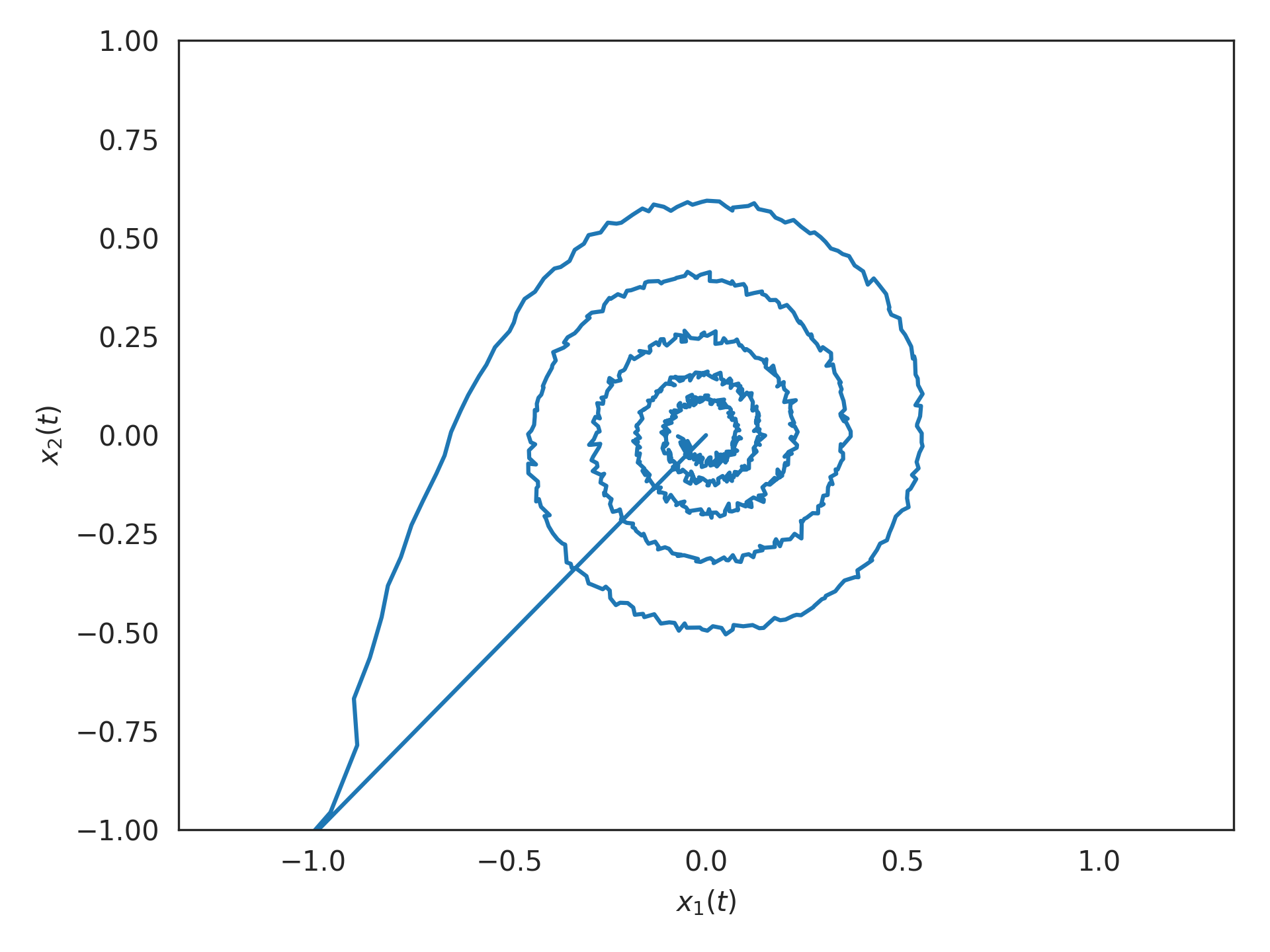
Bandpass()filter (i.e., a decaying 2D oscillator) using 1000 spiking LIF neurons:>>> import nengo >>> from nengolib import Network >>> from nengolib.signal import Balanced >>> with Network() as model: >>> stim = nengo.Node(output=lambda t: 100*int(t < .01)) >>> sys = LinearNetwork(sys=Bandpass(freq=5, Q=10), >>> n_neurons_per_ensemble=500, >>> synapse=.1, dt=1e-3, realizer=Balanced()) >>> nengo.Connection(stim, sys.input, synapse=None) >>> p = nengo.Probe(sys.state.output, synapse=.01) >>> with nengo.Simulator(model, dt=sys.dt) as sim: >>> sim.run(1.)
Note there are exactly 5 oscillations within 1 second, in response to a saturating impulse:
>>> import matplotlib.pyplot as plt >>> plt.plot(*sim.data[p].T) >>> plt.xlabel("$x_1(t)$") >>> plt.ylabel("$x_2(t)$") >>> plt.axis('equal') >>> plt.xlim(-1, 1) >>> plt.ylim(-1, 1) >>> plt.show()
Attributes: AAstate-space matrix of mappedLinearSystem.BBstate-space matrix of mappedLinearSystem.CCstate-space matrix of mappedLinearSystem.DDstate-space matrix of mappedLinearSystem.all_connections(list) All connections in this network and its subnetworks.
all_ensembles(list) All ensembles in this network and its subnetworks.
all_networks(list) All networks in this network and its subnetworks.
all_nodes(list) All nodes in this network and its subnetworks.
all_objects(list) All objects in this network and its subnetworks.
all_probes(list) All probes in this network and its subnetworks.
config(.Config) Configuration for this network.
- dt
A parameter where the value is a number.
inputNengo object representing the input
u(t)to the system.- input_synapse
- label
A parameter where the value is a string.
mappedMapped
LinearSystem.n_neurons(int) Number of neurons in this network, including subnetworks.
outputNengo object representing the output
y(t)of the system.- output_synapse
realizationRealized
LinearSystem.realizer_resultThe
RealizerResultproduced byrealizer.- seed
A parameter where the value is an integer.
size_inInput dimensionality.
size_outOutput dimensionality.
size_stateState dimensionality.
stateNengo object representing the state
x(t)of the system.- synapse
Methods
add(obj)Add the passed object to Network.context.default_config()Constructs a ~.Config object for setting defaults. copy - sys :
