nengolib.synapses.Bandpass¶
-
nengolib.synapses.Bandpass(freq, Q)[source]¶ A second-order bandpass with given frequency and width.
Parameters: - freq :
float Frequency (in hertz) of the peak of the bandpass.
- Q :
float Inversely proportional to width of bandpass.
Returns: - sys :
LinearSystem Second-order lowpass with complex poles.
See also
Notes
The state of this system is isomorphic to a decaying 2–dimensional oscillator with speed given by
freqand decay given byQ.References
[1] http://www.analog.com/library/analogDialogue/archives/43-09/EDCh%208%20filter.pdf Examples
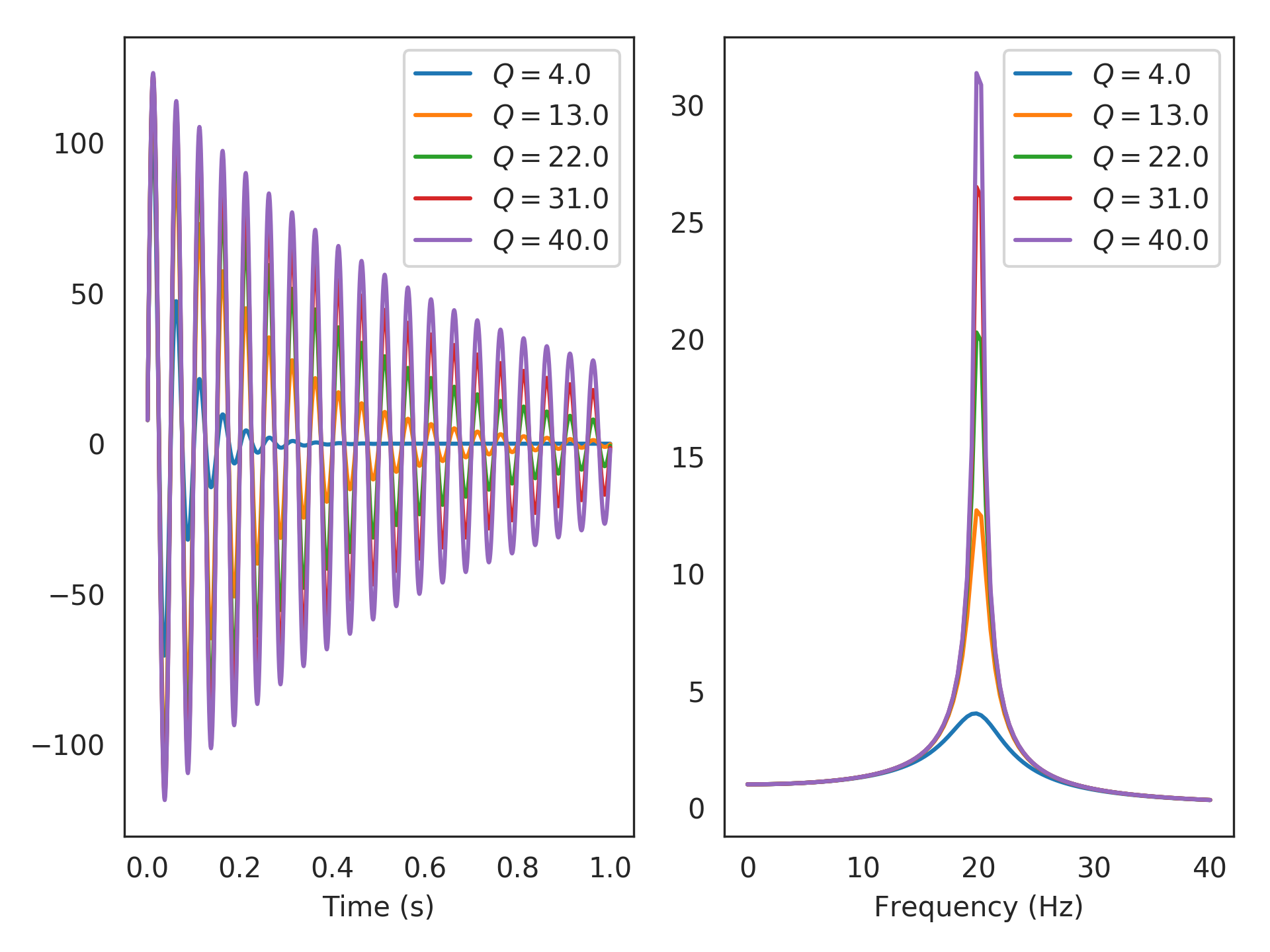
Bandpass filters centered around 20 Hz with varying bandwidths:
>>> from nengolib.synapses import Bandpass >>> freq = 20 >>> Qs = np.linspace(4, 40, 5)
Evaluate each impulse (time-domain) response:
>>> import matplotlib.pyplot as plt >>> plt.subplot(121) >>> for Q in Qs: >>> sys = Bandpass(freq, Q) >>> plt.plot(sys.ntrange(1000), sys.impulse(1000), >>> label=r"$Q=%s$" % Q) >>> plt.xlabel("Time (s)") >>> plt.legend()
Evaluate each frequency responses:
>>> plt.subplot(122) >>> freqs = np.linspace(0, 40, 100) # to evaluate >>> for Q in Qs: >>> sys = Bandpass(freq, Q) >>> plt.plot(freqs, np.abs(sys.evaluate(freqs)), >>> label=r"$Q=%s$" % Q) >>> plt.xlabel("Frequency (Hz)") >>> plt.legend() >>> plt.show()
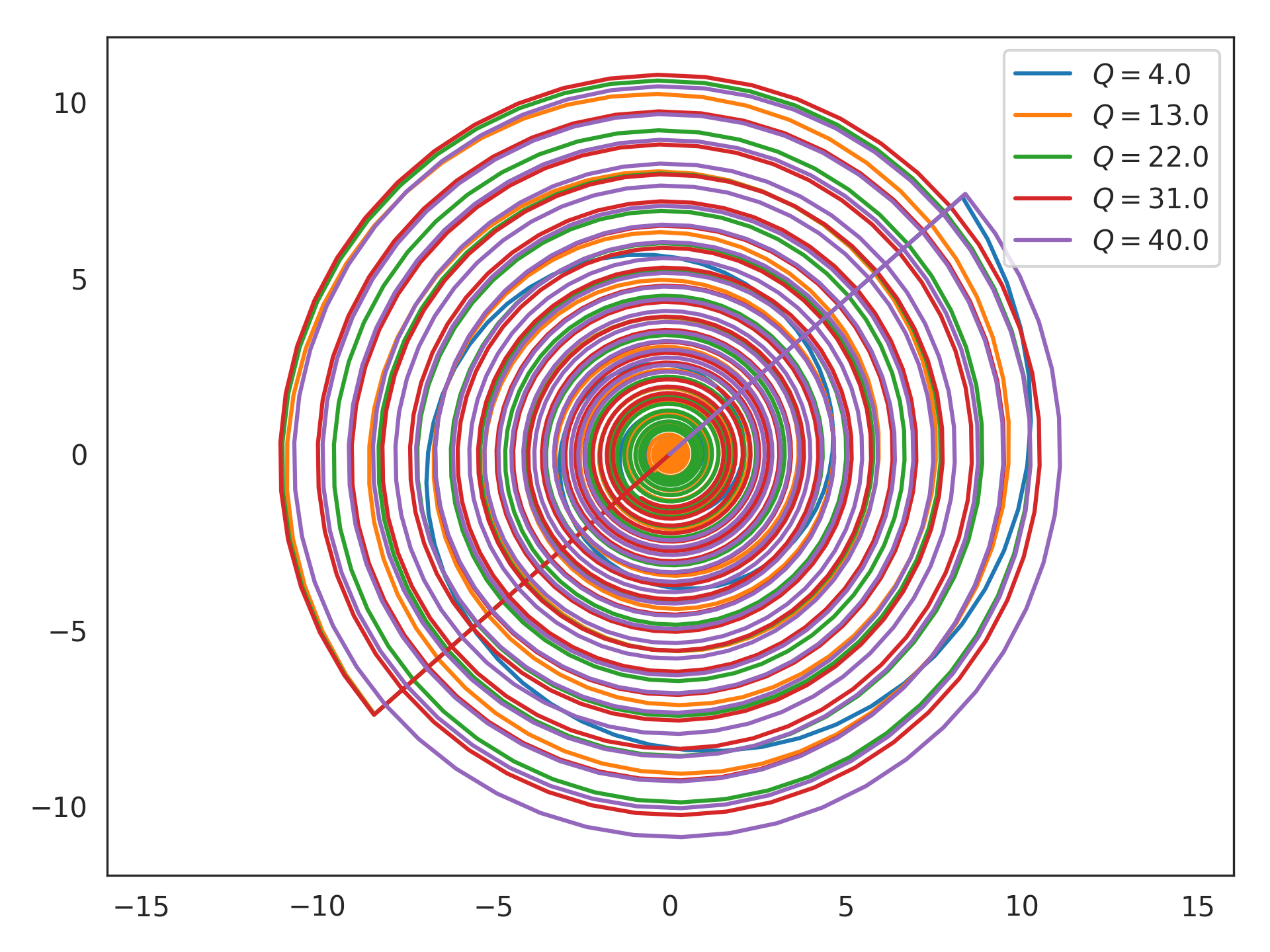
Evaluate each state-space impulse (trajectory) after balancing:
>>> from nengolib.signal import balance >>> for Q in Qs: >>> plt.plot(*balance(Bandpass(freq, Q)).X.impulse(1000).T, >>> label=r"$Q=%s$" % Q) >>> plt.legend() >>> plt.axis('equal') >>> plt.show()
- freq :
